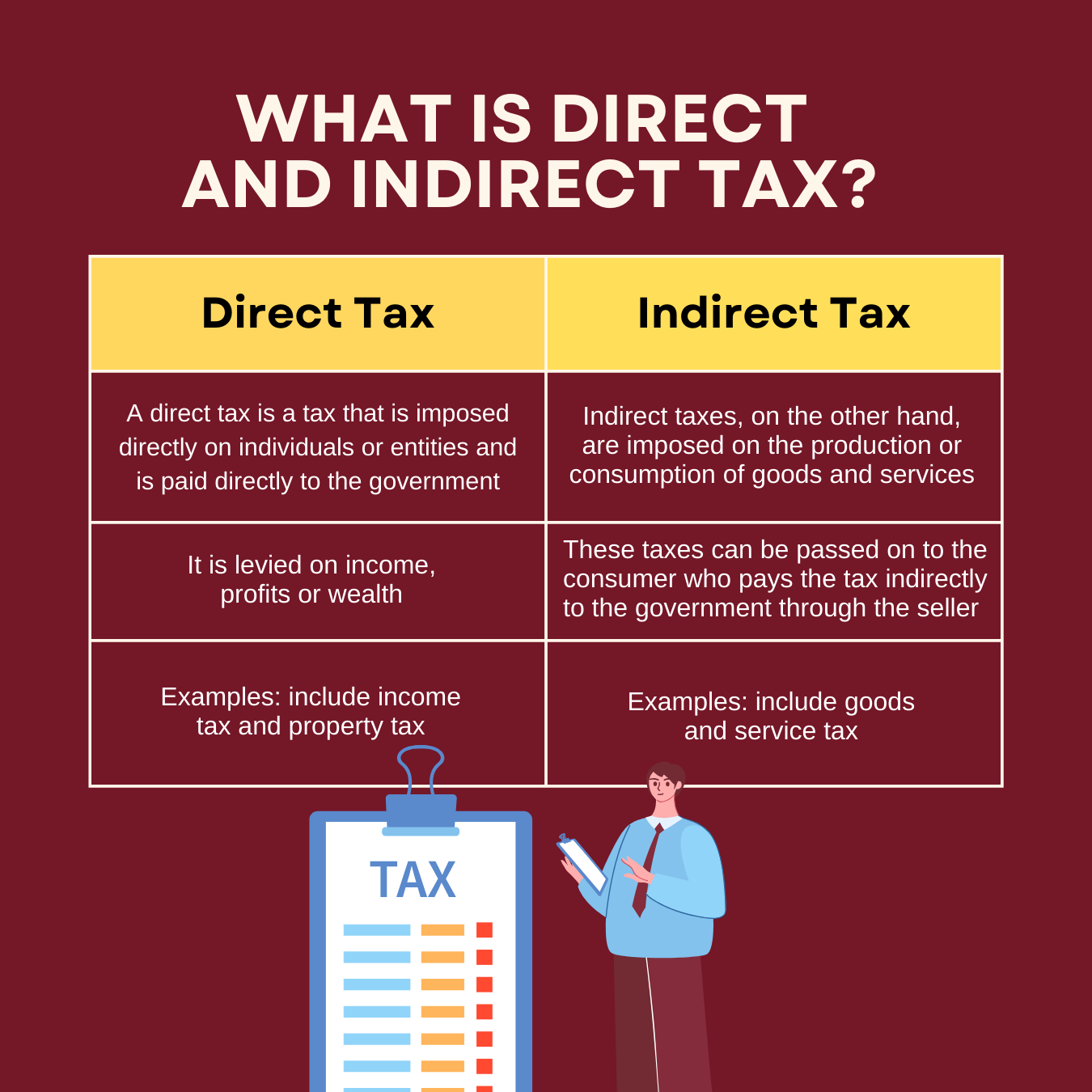
A tax is a compulsory payment imposed by a government on individuals or organizations to generate revenue for public services and infrastructure. Here taxes are divided into direct taxes, levied on individuals or businesses directly, and indirect taxes, collected by intermediaries and passed on to consumers through goods and services.
Table of Contents
- What is Direct and Indirect tax?
- What is Income Tax?
- Who are required to pay Income Tax?
- Categories of income
- What is Financial Year and Assessment Year?
- Income Tax Slab Rates AY 23-24
- Returns Applicable For Filling ITR
- What is TDS?
- What is form 16?
- What is Form 16A?
- What is Advance Tax and Self-assessment Tax ?
- What is the computation of income?
- Why interest under section 234A, 234B, and 234C is applicable while filling ITR?
- What is Late Fee Payable U/s 234F?
- What is ITR-V?

What is Direct and Indirect Tax?
What is Income Tax?
Income tax is a direct tax levied by the government on the income of individuals, businesses, and other entities. It is based on the income earned by a person or entity. Income tax serves as a significant source of revenue for governments, funding public services, infrastructure, and various programs.
Who are required to pay Income Tax?
- Individuals: It has been classified into:
- Individuals less than 60 years of age
- Individuals aged more than 60 but less than 80 years
- Individuals aged more than 80 years
- Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
- Firms
- Companies
- Association of Persons (AOP)
- Body of Individuals (BOI)
- Local Authority
- Artificial Judicial Person
Categories of income
The 5 categories of income as classified by the Income Tax Department are:
| Main Heads | Nature | Example |
| Income from Salary | Amount received from an employer in an employer-employee relationship. | Monthly salary payments fall under this category. |
| Income from Business or Profession | Taxable income derived from a business or profession, with taxation based on net income after deducting expenses. | Profits from a consultancy business. |
| Income from Other Sources | Income from sources like savings account interest, fixed deposits, and lottery winnings. | Interest earned from a savings bank account are taxable. |
| Income from House Property | Income from renting residential or commercial properties is taxable under this head. | Rental income from a property you own. |
| Income from Capital Gains | Taxable profits or gains from the sale of capital assets like houses or shares, categorized as short-term or long-term gains. | Gains from selling a property held as an investment. |
What is Financial Year and Assessment Year?
| Financial Year (FY) | Assessment Year (AY) |
| A one-year accounting period for financial reporting and tax purposes. | The one-year period following the financial year during which taxpayers assess and pay taxes on the income earned. |
| Starts on 1st April of a calendar year and ends on 31st March of the next calendar year. | From 1st April to 31st March immediately after the financial year. |
Income Tax Slab Rates FY 23-24
Under Old Regime
For Individual (resident or non-resident) less than 60 years of age
| Income Tax Slab | Income Tax Rate |
| Up to ₹ 2,50,000 | Nil |
| ₹ 2,50,000 to ₹ 5,00,000 | 5% above ₹ 2,50,000 |
| ₹ 5,00,000 to | 20% above ₹ 5,00,000 + ₹ 12,500 |
| Above ₹ 10,00,000 | 30% above ₹ 10,00,000 + ₹ 1,12,500 |
For Individual (resident or non-resident), 60 years or more but less than 80 years of age
| Income Tax Slab | Income Tax Rate |
| Up to ₹ 3,00,000 | Nil |
| ₹ 3,00,000 to ₹ 5,00,000 | 5% above ₹ 3,00,000 |
| ₹ 5,00,000 to | 20% above ₹ 5,00,000 + ₹ 10,000 |
| Above ₹ 10,00,000 | 30% above ₹ 10,00,000 + ₹ 1,10,000 |
For Individual (resident or non-resident) 80 years of age or more
| Income Tax Slab | Income Tax Rate |
| Up to ₹ 5,00,000 | Nil |
| ₹ 5,00,000 to ₹ 10,00,000 | 20% above ₹ 5,00,000 |
| ₹ 5,00,000 to ₹ 10,00,000 | 30% above ₹ 5,00,000 + ₹ 1,00,000 |
Under New Tax Regime
| Income Tax Slab | Rate of tax | Tax Amount |
| Up to ₹3,00,000 | Nil | Nil |
| ₹3,00,000 to ₹6,00,000 | 5% | ₹15,000 |
| ₹6,00,000 to ₹9,00,000 | 10% | ₹30,000+₹15,000 = ₹45,000 |
| ₹9,00,000 to ₹12,00,000 | 15% | ₹45,000+₹30,000+₹15,000 = ₹ 90,000 |
| ₹12,00,000 to ₹15,00,000 | 20% | ₹60,000+₹45,000+₹30,000+₹15,000 = ₹ 1,50,000 |
| More than ₹15,00,000 | 30% | Income exceeding ₹15,00,000*30% + ₹1,50,000 |
Returns Applicable For Filling ITR
| Return Type | Applicability |
| ITR-1 (SAHAJ) | For resident individuals with a total income up to ?50 lakh, including salary, one house property, and other sources. Applicable for those with agricultural income up to ?5,000. |
| ITR-2 | For individuals and HUFs without income under the business/profession head and ineligible for ITR-1. |
| ITR-3 | For individuals and HUFs with income from business/profession, ineligible for ITR-1, ITR-2, or ITR-4. |
| ITR-4 (SUGAM) | For individuals, HUFs, and firms (excluding LLP) with total income up to ?50 lakh. Applicable for those with presumptive business income (u/s 44AD/44ADA/44AE) and income from specified sources. |
| ITR-5 | Applicable for various entities including firms, LLPs, AOP, BOI, artificial juridical persons, local authorities, cooperative societies, and trusts (except those eligible for ITR-7). |
| ITR-6 | Applicable for companies (Indian or foreign) not claiming exemption under section 11, including body corporates and institutions. |
| ITR-7 | Applicable for individuals and companies required to file returns under specific sections, such as those deriving income from trust for charitable or religious purposes (139(4A)), CEOs of political parties (139(4B)), specified entities under Section 10 (139(4C)), and universities, colleges, or institutions under Section 35 (139(4D)). |
What is TDS?
TDS is a tax collection where a person making a payment deducts a certain percentage of the amount as tax before making the payment. This deducted tax is then deposited with the government on behalf of the payee. TDS is applicable on various incomes such as salaries, interest, rent, and professional fees, ensuring that taxes are collected at the source itself.
What is form 16?
Form 16 is a certificate provided by an employer to an employee at the end of the financial year. It contains details of employee's income, and deductions/exemption. It helps employees in computing their tax liability or refundable amount.
What is Form 16A?
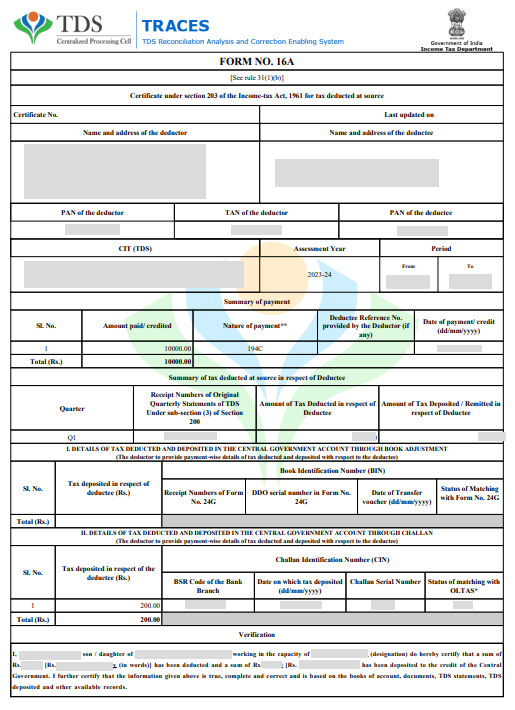
Form 16A is a quarterly TDS certificate which includes details of TDS amount, nature of payments, and information about TDS deposits made with the Income Tax Department. This certificate is provided to the deductee by the deductor for non-salary payments.
What is Advance Tax and Self-assessment Tax ?
|
Advance Tax |
Self-assessment Tax |
| Income tax paid in installments before the end of the financial year. Due dates are June 15 - 15% of advance tax. September 15 - 45% minus previous payments. December 15: - 75% minus previous payments. March 15 - 100% minus previous payments. | Tax paid online to fulfill outstanding dues before submitting the income tax return, ensuring completeness of the filing process. |
What is the computation of income?
The computation of income involves a presentation of an assessee's personal details, bank account information, income details, and the calculation of taxes.
| Basic Details |
| Assessee Name | -------------------- |
| Father Name | -------------------- |
| Address | -------------------- |
| Permanent Account Number | -------------------- |
| Date of Birth | -------------------- |
| Financial Year | -------------------- |
| Assessment Year | -------------------- |
| Aadhaar Number | -------------------- |
| Computation of Total Taxable Income for the year ended 31st March |
| Particular | Amount in Rs |
| INCOME FROM SALARY | |
| Gross Salary as per form No. 16 | |
| Add: Perquisits, Other Allowances, Profit on lieu of Salary | |
| Less: Allowances Exempt U/S 10 | |
| Less: Deduction U/S 16 ( Tax on Employment) | |
| Less : Standard Deduction | |
| INCOME FROM HOUSE PROPERTY | |
| Let Out | |
| Less: Interest on loan borrowed for | |
| Construction of house | |
| Less: Corporation Tax | |
| Less: Standard Deduction | |
| INCOME FROM BUSINESS \ PROFESSION | |
| Net Profit as per Profit and Loss Account | |
| Add: Disallowable / Items Considered Seperately | |
| Depreciation Considered Seperately | |
| Less: Allowable / Items Considered Seperately | |
| Depreciation as per Income Tax Act | |
| INCOME FROM OTHER SOURCE | |
| Fixed Deposit Interest | |
| Interest on Saving Bank | |
| Dividend | |
| GROSS TOTAL INCOME | |
| DEDUCTION CHAPTER VIA | |
| Section 80C | |
| Life Insurance Premium | |
| PPF (Public Provident Fund) | |
| EPF (Employees’ Provident Fund) | |
| Repayment of Home Loan | |
| Children’s Tuition Fees | |
| Sukanya Samriddhi Deposit Scheme | |
| National Savings Certificates (NSC) | |
| Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS) | |
| SCSS (Post office Senior Citizen Savings) | |
| PLI (Postal Life Insurance) | |
| Any Other (Specified) | |
| Section 80CCC | |
| Section 80CCD(1) | |
| Section 80CCD(1B) | |
| Section 80CCD(2) | |
| Section 80CCG | |
| Section 80D - Mediclaim | |
| Section 80DD | |
| Section 80DDB | |
| Section 80E - Int. on Education Loan | |
| U/S 80EE - Int. on House Property | |
| Section 80G - Donation Paid | |
| Section 80GG - Rent Paid | |
| U/S 80GGC - Paid to Political Party | |
| Section 80TTA - Saving Interest | |
| Section 80TTB - FD Interest (Only for Senior Citizen) | |
| Section 80U - Self With Disability | |
| TOTAL TAXABLE INCOME | |
| TAX ON TOTAL INCOME | |
| Income Tax on Total Income | |
| Less : Tax Rebate on Agricultural Income | |
| Less: Income Tax Rebate u/s 87A | |
| Tax Payble on Total Income | |
| Add: Education Cess @ 4% | |
| INTEREST PAYABLE | |
| U/s 234A | |
| U/s 234B | |
| U/s 234C | |
| Late Fee Payable U/s 234F | |
| TAXES PAID | |
| Advance Tax | |
| TDS/ TCS | |
| Self Assessement Tax | |
| TAX PAYABLE / (REFUNDABLE) |
Why interest under section 234A, 234B, and 234C is applicable while filling ITR?
Interests under sections 234A, 234B, and 234C are applicable while filing an Income Tax Return (ITR) for the following reasons:
- Section 234A: Applies for a delay in filing the return of income.
- Section 234B: Applies to non-payment or short payment of advance tax.
- Section 234C: Applies to non or short payment of one or more than one installments of advance tax.
What is Late Fee Payable U/s 234F?
Section 234F imposes a late fee for delayed filing of Income Tax Return.
The penalty is Rs.5,000, but it reduces to Rs.1,000 if the income is below Rs.5 lakh.
It's an additional amount to be paid along with interest for late filing.
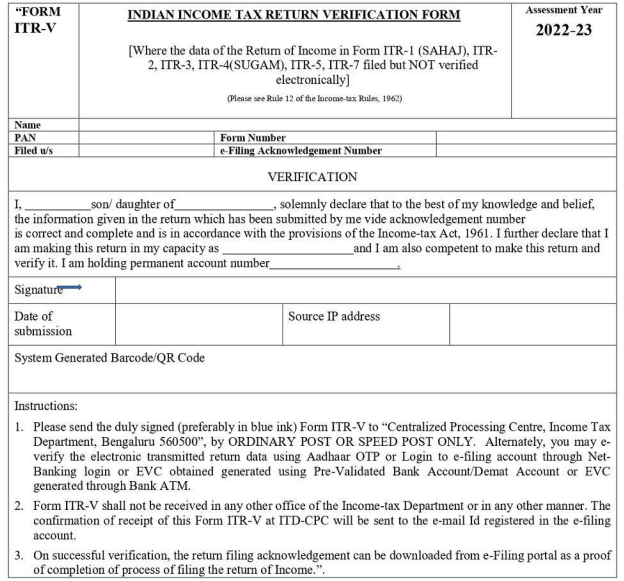
What is ITR-V?
Form ITR-V is the 'Income Tax Return-Verification' form which is received when an online tax return is filed without a digital signature.
Taxpayers receive ITR-V through email or can download it from the income tax e-filing website.
Verification is crucial, and it can be done manually by sending a signed copy of ITR-V to the Income Tax Department CPC, Bangalore, or online.








 CAclubindia
CAclubindia
