Consolidated financial statements
(CFS) which lead to the subsidiaries of the holding company its summative accounting figure. Putting another way, consolidated financial statements can be addressed as the combined financial statements of a parent company and its subsidiaries.
Financial statements of a group in which the assets, liabilities, equity, income, expenses and cash flows of the parent (company) and its subsidiaries are presented as those of a single economic entity", according to International Accounting Standard 27 "Consolidated and separate financial statements", and International Financial Reporting Standard 10 "Consolidated financial statements".
According to IAS 27 "Consolidated and separate financial statements", consolidated financial statements are the financial statements of a group presented as those of a single economic entity.
In the preparation of CFS, other relevant accounting standards shall apply. The CFS shall be prepared in addition to separate financial statements of the parent and its subsidiaries. The CFS should be prepared for both domestic as well as foreign subsidiaries. Subsidiaries should not be excluded from consolidation merely on the ground that business activities of parent and subsidiary are dissimilar.
The key purpose of preparing consolidated financial statements is reporting the financial condition and operating result of a consolidated business group, which is considered as a single entity comprised of more than one companies under a common control (also counting entities other than “companies”).Consolidation would prove beneficial to the users of financial statements. Elimination of intra-group transaction is the hallmark of consolidation.
CFS enables to determine the general health of an entire group of companies as compared to a company’s stand alone position. This is because these financial statements provide an aggregated look at the financial position of a company and its subsidiaries.
Corporate Restructuring
Corporate restructuring is the process of redesigning one or more aspects of a company. The process of reorganizing a company may be implemented due to a number of different factors, such as positioning the company to be more competitive, survive a currently adverse economic climate, or poise the corporation to move in an entirely new direction.
Restructuring a corporate entity is often a necessity when the company has grown to the point that the original structure can no longer efficiently manage the output and general interests of the company. For example, a corporate restructuring may call for spinning off some departments into subsidiaries as a means of creating a more effective management model as well as taking advantage of tax breaks that would allow the corporation to divert more revenue to the production process.
In this scenario, the restructuring is seen as a positive sign of growth of the company and is often welcome by those who wish to see the corporation gain a larger market share.
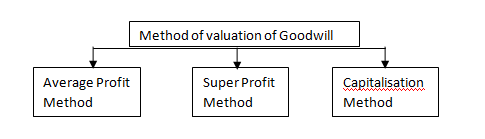
Valuation of Goodwill
Goodwill is the value of the reputation/credit worthiness of a firm in respect of the profits expected in future over and above the normal profits earned by other similar firms belonging to the same industry. Such excess of future profits referred as “Super profits”.If time value of money is considered, goodwill can be defined as the present value of anticipated super profits. Goodwill arises when one company acquires another, but pays more than the fair market value of the net assets (total assets - total liabilities). It is classified as an intangible asset on the balance sheet.
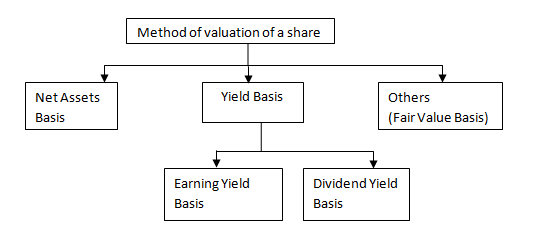
Valuation of Shares
Share valuation based on fundamentals aims to give an estimate of their intrinsic value of the shares, based on predictions of the future cash flows and profitability of the business. Fundamental analysis may be replaced or augmented by market criteria – what the market will pay for the shares, without any necessary notion of intrinsic value. These can be combined as "predictions of future cash flows/profits.
Valuation of Brand
In this competitive business environment the key to success and survival of an entity is the image of their brands. Since the brand gives tremendous competitive advantage to entity. It can be said that rather than product selling itself, it is brand that sells the product. Brands are strategic assets.
Corporate Brand Accounting refers to “the practice of valuation and reporting of the value of brand of a product o5r service in the financial statements of a corporate entity, the value of a brand being ascertained either as a result of revaluation in case of home-grown brands or as a result of acquisition/merger in case of newly acquired brands.
Valuation of Business
Business valuation is a process and a set of procedures used to estimate the economic value of an owner’s interest in a business. Valuation is used by financial market participants to determine the price they are willing to pay or receive to affect a sale of a business.
Employee Share Based Payments
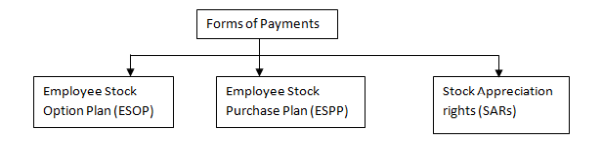
An employee stock ownership plan (ESOP) is an employee-owner scheme that provides a company's workforce with an ownership interest in the company. In an ESOP, companies provide their employees with stock ownership, often at no up-front cost to the employees. ESOP shares, however, are part of employees' compensation for work performed. Shares are allocated to employees and may be held in an ESOP trust until the employee retires or leaves the company. The shares are then sold.
A company-run program in which participating employees can purchase company shares at a discounted price. Employees contribute to the plan through payroll deductions, which build up between the offering date and the purchase date. At the purchase date, the company uses the accumulated funds to purchase shares in the company on behalf of the participating employees. The amount of the discount depends on the specific plan but can be as much as 15% lower than the market price.
Value Added Statement (VAS)
Value Added is the wealth which a reporting entity has been able to create through the collective effort of resources (ie capital, management and employee).
In economic terms, VA is the market price of the output of an enterprise less the price of the goods and services acquired from the outside suppliers. VA arises due to input-output relationship with various stakeholders (such as employees, directors, govt., financiers).
Economic Value Added (EVA)
EVA is primarily a benchmark to measure earnings efficiency.EVA as a residual income measure of financial performance is simply the Operating profit after tax less a charge for the Operating capital employed, used in the business.
Human Resource Accounting (HRA)
HRA is an attempt to identify, quantify and report investments made in human resources of an organizations. Leading public sector units like OIL, BHEL, NTPC and SAIL etc. have started reporting human resource in their annual reports as additional information.
Click Here to view Rahul Malkan's Class on Financial Reporting








 CAclubindia
CAclubindia
