Price to Earning (P/E) ratio = price (per share) ÷ earnings (per share).
Low P/E ratio indicates that the stock is undervalued (or the company is failing).
Consider the example, if a company’s share price is 200 Rs and its earning per share is Rs 20 in last 12 month. Its P/E ratio will be 200 ÷ 20 = 10.
The P/E ratio answers the question “Am I paying too much for the company’s earnings?”
Some points to remember:
1. Don’t invest in those company’s share which is having much higher value of Price to Earning (P/E) ratio compared to other stocks in same category because it indicates that current price of the share is overvalued, price of that stock have more chances to fall in future.
2. Don’t invest in those company’s share with no price to earning value. No P/E value means that the company is in loss.
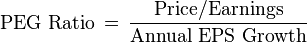


 CAclubindia
CAclubindia
