Even though exempt income is not taxable, but you must mandatorily disclose in the Income Tax Return under the “Exempt Income” Schedule to ensure transparency and avoid tax notice in future.
Reason for Disclosure
Non-disclosure may trigger mismatch with AIS/TIS (Annual Information Statement/Tax Information Statement) and lead to income tax notices, delayed refunds, or scrutiny.
Disclosure of tax free income helps to avoid notices in case you have large receipt. Say for example – Matured PPF received in saving account above Rs.50 Lakh and that is shown in AIS/TIS under SFT as Bank reports the same.
No Penalty For Non-Reporting of ITR
There is no penalty for non-reporting in ITR but if disclosed it becomes easier to explain the source of funds in future such as high value exempt income.
AIS may already have records of exempt income, if you do not show in ITR, it may trigger notice for “information mismatch” and can delay in processing refunds.
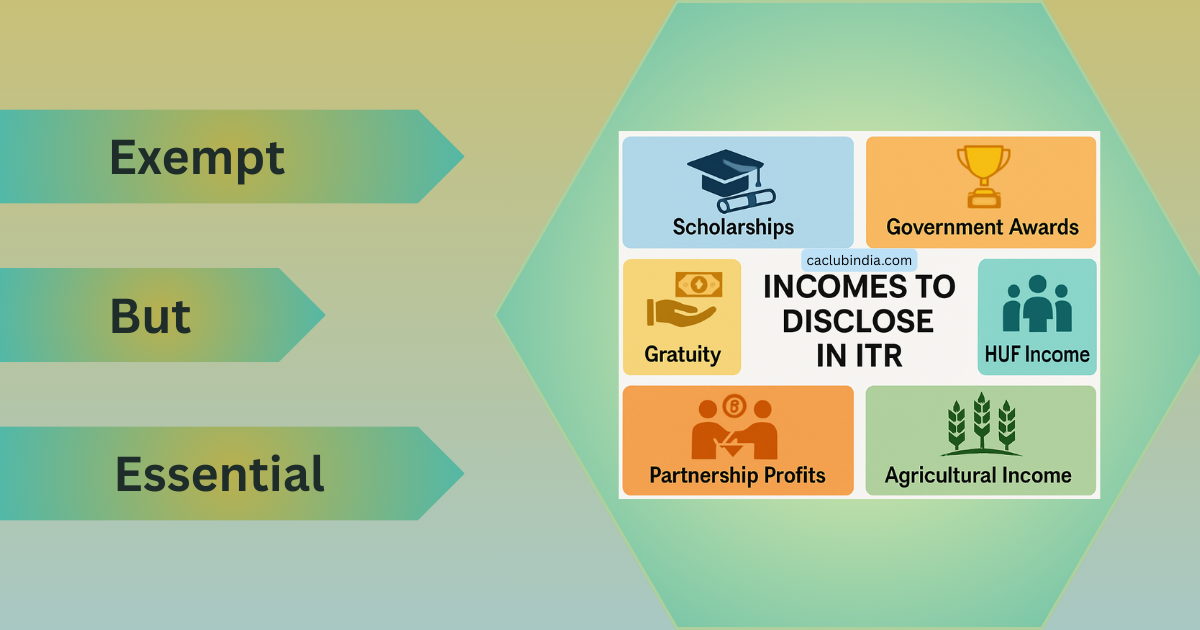
Which are Those Fully Exempt Income Required to be Disclosed?
- PPF Interest and maturity u/s 10(11)
- PF Receipts u/s 10(11)
- Withdrawal from PF Fund after 5 Years u/s 10(12)
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana Interest and Maturity u/s 10(11A)
- LIC Maturity Received u/s 10(10D) – Exempt if Premium up to 10% Sum
- Leave Encashment on Retirement u/s 10(10AA) – Fully Exempt Government and partly for Others
- Retrenchment Compensation u/s 10(10B) – Exempt up to Specified Limit
- VRS Receipts u/s 10(10C) – Exempt Up to Rs. 5 Lakh Once in Lifetime
- Tax Free Bond Interest u/s 10(15) – NHAI, REC
- Gifts Received from Relatives as per section 56(2)(x) – Cash gift limits 2 Lakh, unlimited through online transfer
- Scholarships u/s 10(16)
- Awards and rewards approved by Government. u/s 10(17A)
- Gratuity u/s 10(10) – Exempt Up to Rs. 20 Lakh for Non-Government.
- HUF Income u/s 10(2) – Exempt if received as a member of HUF.
- Share of Profit from a Partnership Firm u/s 10(2A) – Exempt in Partner’s Hands but Firms need to Pay Tax
- Agricultural Income u/s 10(1) – Fully Exempt, but if exceeds 5000 must be disclosed in ITR.
Conclusion
Showing exempt income in ITR provides transparency, prevents mismatch with AIS, safeguards against future notices, and establishes a clear source of funds for high-value receipts.