Golden Rules of Accounting provide a framework for accurately recording financial transactions in accounting books, ensuring consistency and clarity in financial reporting.
Book-keeping and accounting should not be confused as one. Book-keeping is a part of accounting which involves recording of business transactions where accounting is a broader term used to entire accounting system.
What are the Golden Rules of Accounting?
The golden rules of accounting are principles that helps to guide in recording of financial transactions.
The rules ensure consistency and accuracy in recording transactions, and helps to maintain the fundamental accounting equation. The rules can be better understood from the type of accounts under different approaches.

Classification of accounts
There are two approaches for the classification of accounts:
-
- Traditional Approach
-
- Modern Approach
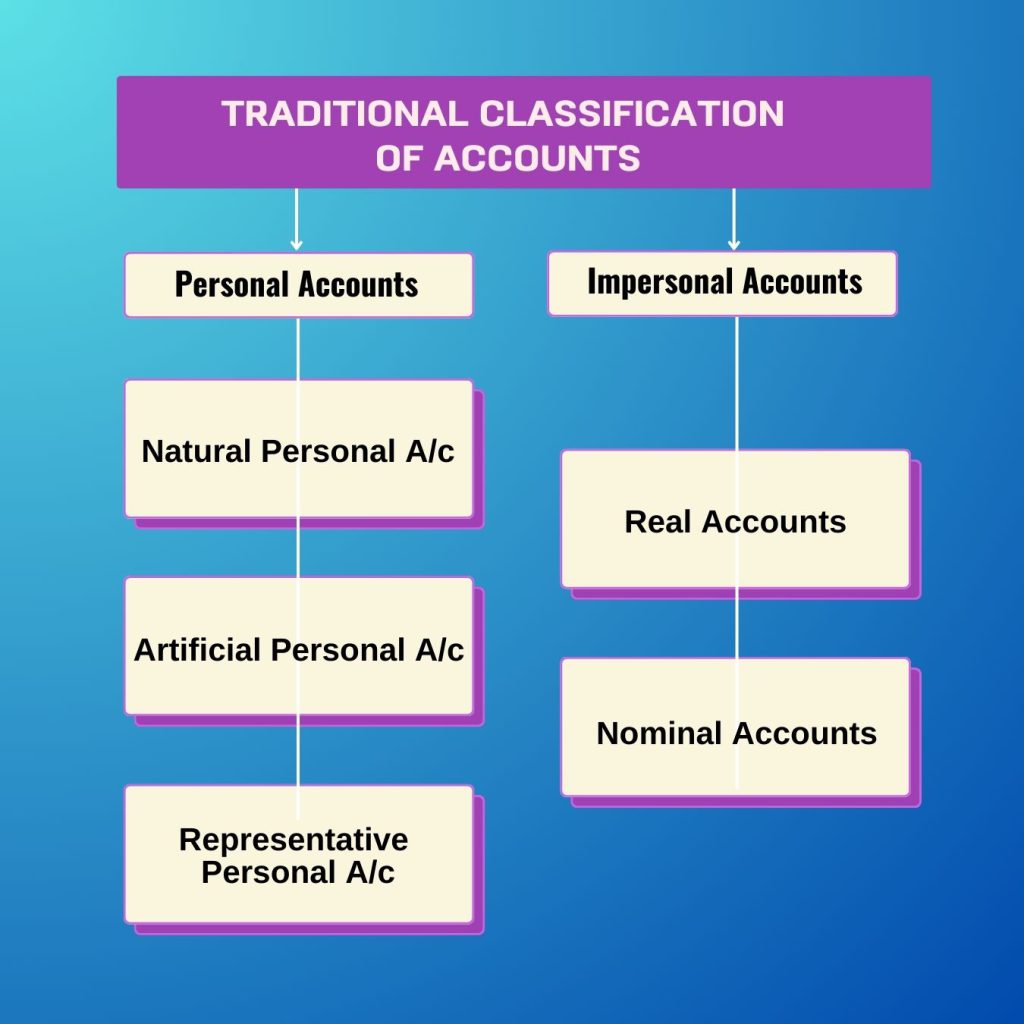
Traditional Approach
The classification of traditional approach are:
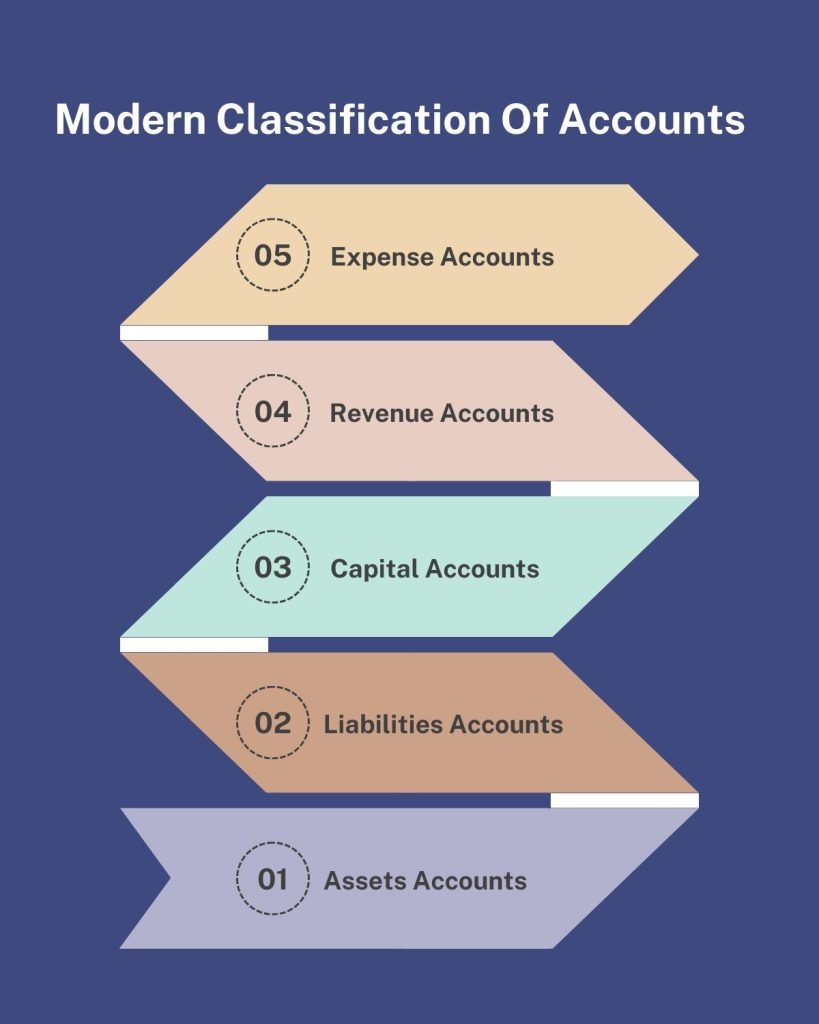
Modern Approach
Modern approach accounts are classified into five category:
Rules for Debit and Credit
As there are two approaches for classification of accounts heads, the rules applicable for debit and credit considered different.
-
- Golden Rule of Accounting or Golden Rule of Debit and Credit under Traditional Approach
-
- Rule of Debit and Credit under Modern Approach
Golden Rules of Accounting or Golden Rule of Debit and Credit under Traditional Approach
The rules for debit and credit under traditional approach are termed as golden Rules of Debit and Credit. The Rules are:
| Accounts Type | Golden Rule |
| Personal Accounts | Debit – The receiver of the benefit Credit – The giver of the benefit |
| Real Accounts | Debit – What comes in Credit – What goes out |
| Nominal Accounts | Debit – Expenses and Losses Credit – Gains and Incomes |
Rule of Debit and Credit under Modern Approach
| Accounts Type | Rule |
| Assets Accounts | If there is an increase in the asset, it is “Debited”. If there is a decrease in the asset, it is “Credited”. |
| Liabilities Accounts | If there is an increase in the liability, it is “Credited”. If there is a decrease in the liability, it is “Debited”. |
| Capital Accounts | If there is an increase in the capital, it is “Credited”. If there is a decrease in the capital, it is “Debited”. |
| Revenue Accounts | If there is an increase in the revenue, it is “Credited”. If there is a decrease in the revenue, it is “Debited |
| Expenses Accounts | If there is an increase in the expense, it is “Debited”. If there is a decrease in the expense, it is “Credited”. |
Table showing the accounts to be Debited/ Credited under Traditional & Modern approach
| Account Head | American Approach/ Modern Approach | English Approach/ Traditional Approach | Debit / Credit |
| (A) Increase in the balance of account | |||
| Rent Received | Revenue a/c | Nominal a/c | Credit |
| Motor Vehicles a/c | Asset a/c | Real a/c | Debit |
| Proprietor’s a/c | Capital a/c | Personal a/c | Credit |
| Suresh (Debtor) | Asset a/c | Personal a/c | Debit |
| Jayant (Creditor) | Liability a/c | Personal a/c | Credit |
| (B) Decrease in the balance of account | |||
| Wages Paid | Expenses a/c | Nominal a/c | Credit |
| Proprietor’s a/c | Capital a/c | Personal a/c | Debit |
| Furniture a/c | Asset a/c | Real a/c | Credit |
| Ranjan (Creditor) | Liability a/c | Personal a/c | Debit |
| Anand (Debtor) | Asset a/c | Personal a/c | Credit |
Analysis of Transactions According to Traditional & Modern Approach
-
- Transactions – Pulkit started business.
| Accounts Affected | Classes of accounts Under Traditional Approach | Classes of accounts Under Modern Approach |
| Cash Capital |
Real (comes in) Personal (Giver) |
Asset (Increased) Capital (Increased) |
-
- Transaction – Purchase Machinery in cash.
| Accounts Affected | Classes of accounts Under Traditional Approach | Classes of accounts Under Modern Approach |
| Machinery Cash |
Real (Comes in) Real (Goes out) |
Asset (Increased) Asset (Decreased) |
-
- Transaction – Withdrawn from Bank for office use.
| Accounts Affected | Classes of accounts Under Traditional Approach | Classes of accounts Under Modern Approach |
| Cash Bank |
Real (Comes in) Personal (Giver) |
Asset (Increased) Asset (Decreased) |
What is Journal?
Journal is a book of original entry in which transactions are recorded in chronological order from source documents showing the accounts to be debited and credited in a systematic manner.
Steps involved in Journalising
There are three steps involved in the process of journalising a transaction.
Step 1 : Identification of accounts or ‘accounts heads’ affected by the transaction.
Step 2 : Classification of accounts or accounts heads.
Step 3 : Application of Rules for Debit or Credit.
Illustration : On 03-04-2024, Anil purchased furniture for Cash Rs. 20,000.
Solution :
| Date | Particulars | L. F. |
Dr. Amount |
Cr. Amount |
| 03 Apr 2024 | Furniture A/c………………..Dr. To Cash A/c (Being furniture purchased in cash) |
20,000 | 20,000 |
Explanation :
Step 1 : Identification of accounts or ‘accounts heads’ affected by the transaction
In this transaction, the business has paid cash for purchase of furniture. Here, the two accounts involved are ‘Furniture A/c’ and ‘Cash A/c’.
Step 2 : Classification of accounts or accounts heads
According to Traditional classification or Golden Rule of Debit and Credit, Furniture A/c’ is a Real Account and ‘Cash A/c’ is a Real Account.
According to Modern classification, ‘Furniture A/c’ is a Asset Account and ‘Cash A/c’ is a Asset Account.
Step 3 : Application of Rules for Debit or Credit
According to Traditional classification : Furniture being asset comes in the business so, ‘Furniture A/c’ will be debited and as cash goes out ‘Cash A/c’ will be credited.
According to Modern classification : Asset increases as Furniture has been brought, “Furniture A/c’ will be debited and as the asset in the form of cash decreases because cash has been paid, ‘Cash A/c’ will be credited.