Tariff is generally tax imposed by a government on goods and services that are imported from other country.
US President Donald Trump has made headlines by saying that he will impose 25% tariff on iPhone if they manufactured outside the US.
Statement From Trump
Apple will not be given any exception, if iPhones are not made in the USA, a tariff of at least 25% will be applied.
He also warned Apple and other smartphone makers like Samsung that tariff will be applied on iPhones sold in the United States if they are manufactured outside the country, specifically targeting production in India.
Apple’s Current Strategy
Apple want to focus in India as:
- India is already producing 15-25% of all iPhone.
- Apple’s also plans to manufacture 50-60% of iPhone for US market in India by 2026.
- Apple’s main suppliers are in India, including Foxconn, Pegatron and Wistron, etc have significantly ramped up production.
Why they choose India?
Apple choose India Because of:
- Lower production cost.
- Government incentives under PLI Scheme.
Impact on Trump’s Statement
Market Impacts
The announcement led to immediate market reactions, with Apple’s stock fell by approx. 3% in early trading on 23rd May 2025.
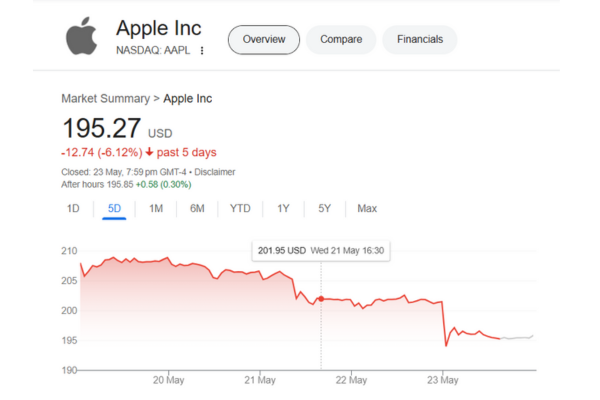
Consumer Impact
Price increases would hurt US consumers.
For India
This could slow down the iPhone export boom that was helping India’s goal to become a global electronic hub.
Why Tariffs Imposed?
Governments impose tariffs for several reasons:
- For revenue generation.
- Raising the price of imported goods, tariffs make domestic products more competitive.
- It can serve as a foreign policy tool, pressuring trading partners to adjust policies.
- Tariffs can address issues like foreign subsidies or dumping, where goods are sold below cost to undercut local markets.
Then What is Reciprocal Tariffs?
Reciprocal tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods from countries that impose higher tariffs on U.S. export.
Effective
On 2nd April 2025, President of America Donald Trump has announced comprehensive set of tariffs which is termed as reciprocal tariffs.
Focus
- To target countries that impose higher tariffs on US exports.
Trump’s reasoning – “if they tax us, we tax them the same – or more”
Benefits For America
- This policy is part of Trump’s broader “America First” Trade Strategy.
- It is a response to decades of trade deficits and what Trump calls “unfair trade practices” by foreign government.
- He believes this move will revive American industry, bring manufacturing back and protect U.S. jobs.
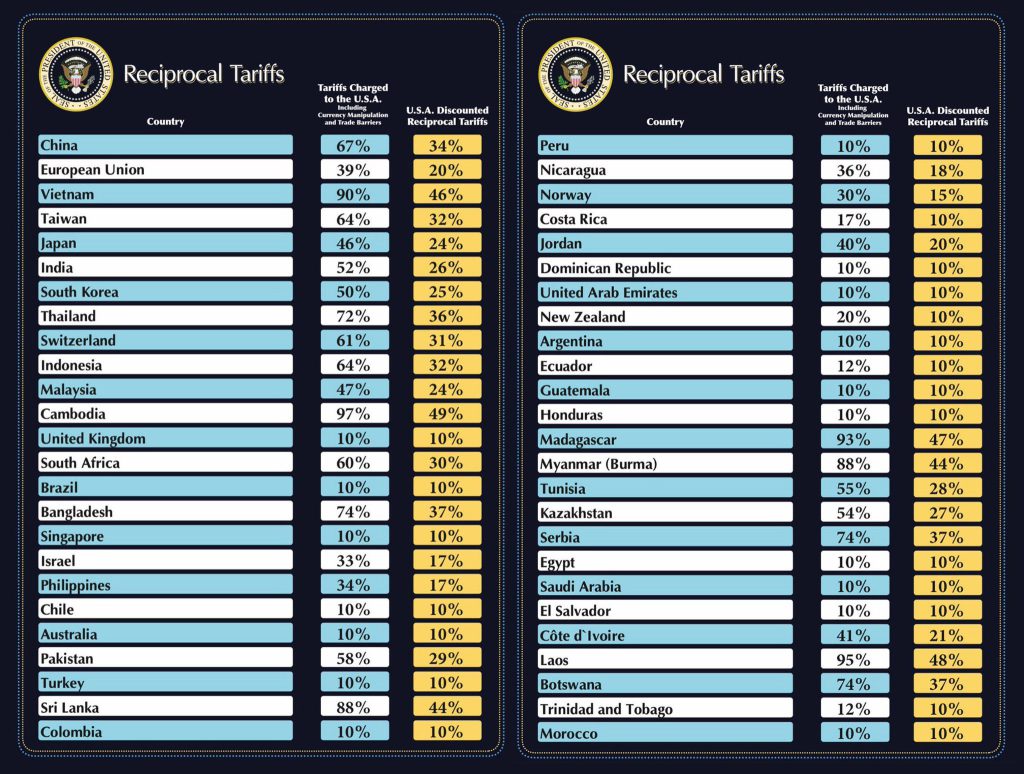
Country’s Specific Tariffs
Conclusion
Trump’s reciprocal tariffs mark a significant shift in U.S. trade policy, aiming to counter high foreign duties.
India’s exports, particularly in key sectors, may face challenges due to the tariff.
The move could escalate trade tensions, prompting renegotiations or policy adjustments.
